With the ever-growing popularity of mobile applications, iOS remains one of the most lucrative platforms for app developers. Apple’s ecosystem, known for its high performance and dedicated user base, encourages companies and independent developers to create stunning, intuitive, and efficient iOS apps. However, choosing the best iOS programming language is critical to building scalable, reliable, and user-friendly applications.
This blog will explore the top iOS programming languages that dominate the field. Whether you are a business owner looking for the best language for iOS app development or a developer interested in broadening your skill set, understanding each language’s features, pros, and cons is crucial.
Why Choose iOS for App Development?
Choosing iOS for app development offers several advantages, including access to a high-value user base with strong purchasing power. iOS provides a streamlined development process with a uniform hardware ecosystem and less device fragmentation. It enables faster testing and quality assurance, ensuring robust app performance across devices.
Additionally, Apple’s strong focus on security and regular updates helps maintain app security and compliance with global regulations. App Store’s stringent quality guidelines also enhance app visibility and trust.
- Based on Statista’s projections, the global smartphone user count is anticipated to grow by 1.7 billion over the period from 2024 to 2029.
- The global smartphone market size is expected to grow from USD 510 billion in 2022 to about USD 876 billion by 2032, with a projected CAGR of 5.70% for 2023-2032.
- The valuation of the global mobile application market stood at USD 252.89 billion in 2023, with an anticipated compound annual growth rate of 14.3% from 2024 to 2030.
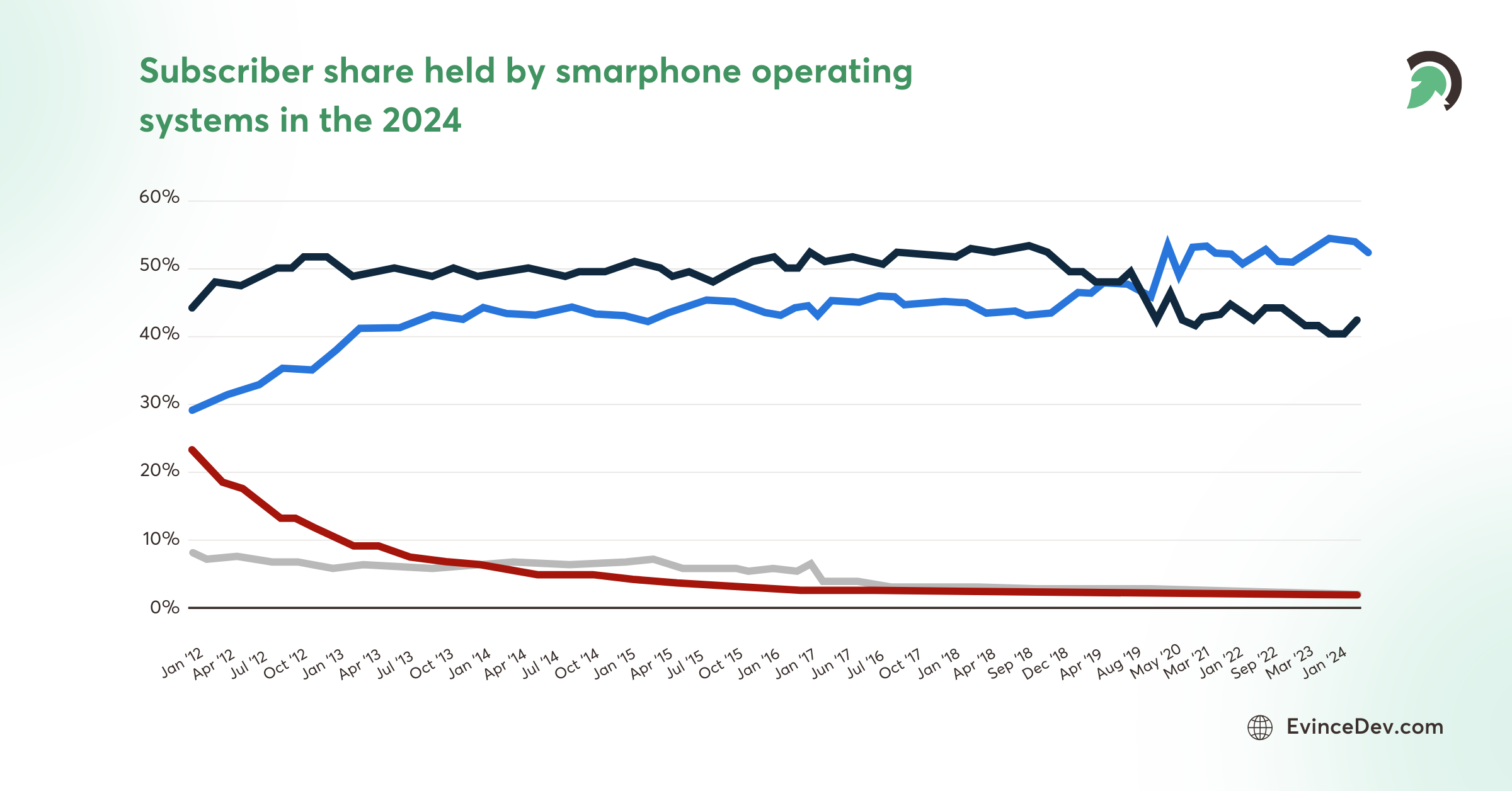
- By March 2024, iOS continued to lead the smartphone operating system market in the U.S., securing over 50% of the market.
Exploring the numerous iOS programming languages can feel complex, but five stand out for their notable advantages and tailored use cases:
1. Swift: Apple’s Official Programming Language for iOS
Swift is the primary programming language used for iOS development. Introduced by Apple in 2014, Swift was designed to replace Objective-C and provide developers with a modern, powerful, and more intuitive programming experience. Swift has rapidly gained popularity due to its ease of use, safety features, and performance enhancements.
Why Choose Swift for iOS Development?
- Performance: Swift is optimized for performance, offering speeds comparable to C++ and up to 2.6 times faster code execution than Objective-C for everyday tasks.
- Safety: Swift reduces the likelihood of programming errors by implementing strict typing and error-handling mechanisms, making it a safer language.
- Interoperability: Swift is fully compatible with Objective-C, allowing developers to mix both languages in a single project. This is particularly useful when maintaining legacy code.
- Open-Source: Swift is continuously improved by the community and Apple as an open-source language, making it highly reliable and future-proof.
Who Should Use Swift?
If you’re aiming to develop iOS apps quickly with fewer bugs and modern language features, Swift is the best language for iOS app development. It’s especially ideal for developers working on new projects or upgrading older apps for enhanced performance and maintainability.
Popular Use Cases for Swift
- Native iOS, macOS, watchOS, and tvOS applications
- Mobile app development services focused on creating high-performance apps
- iOS app development companies delivering scalable and optimized solutions for clients
2. SwiftUI: Apple’s Modern Framework for Declarative UI Development
SwiftUI is a user interface toolkit introduced by Apple in 2019. It enables developers to create responsive and visually engaging UIs across iOS, macOS, watchOS, and tvOS. As a declarative framework, SwiftUI allows developers to build interfaces by specifying what the UI should look like rather than how it should be constructed, simplifying the code structure and enhancing readability.
Why Choose SwiftUI for iOS Development?
- Declarative Syntax: SwiftUI’s declarative syntax lets developers create complex UIs with less code, reducing development time and making code easier to understand and maintain.
- Seamless Integration with Swift: SwiftUI integrates seamlessly with Swift, Apple’s primary programming language, allowing developers to leverage Swift’s performance and safety features while building user interfaces.
- Real-time Previews: SwiftUI’s design canvas in Xcode provides real-time previews, allowing developers to visualize and modify their UI instantly, which speeds up the development cycle and ensures better alignment with design requirements.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Since SwiftUI is available across Apple’s platforms, it enables code reuse and a consistent user experience, which is particularly beneficial for multi-platform applications.
SwiftUI Use Cases
SwiftUI is ideal for developers and companies focusing on creating visually stunning, modern applications that benefit from Apple’s latest advancements in UI technology. It’s particularly suited for:
- Building modern, responsive UIs in iOS, macOS, and watchOS applications.
- Fast prototyping due to its live preview functionality.
- Cross-platform projects where a unified codebase across Apple platforms is a priority.
SwiftUI is rapidly becoming popular among developers who want to adopt the latest Apple UI technologies and build future-proof, high-performance applications.
3. Objective-C: The Legacy Language
Before Swift, Objective-C was the go-to language for iOS app development. Although Swift has largely replaced it for new projects, Objective-C remains relevant for maintaining and updating older applications, especially in large companies with substantial codebases written in this language.
Strengths of Objective-C
- Mature Ecosystem: Objective-C has been around since the late 1980s, and its longevity means that it has a well-established ecosystem with extensive libraries and tools.
- C Interoperability: Objective-C is built on top of C, allowing it to easily interface with C-based libraries, which can be helpful in specific low-level tasks.
- Legacy Code Support: If your app was initially developed in Objective-C, it’s often easier to maintain and update it in the same language.
Limitations of Objective-C
- Complex Syntax: Objective-C’s syntax is considered outdated by modern standards, making it harder to learn and use than Swift.
- Slower Development: The language requires more boilerplate code, leading to slower development times.
Objective-C Use Cases
Objective-C is still a practical option for iOS app development services if you maintain legacy applications or require seamless integration with older C/C++ libraries.
4. Flutter and Dart: Google’s Cross-Platform Solution
Flutter is a popular framework developed by Google that uses Dart as its programming language. Although initially created for Android development, Flutter has gained traction among iOS developers due to its fast rendering engine and single codebase for both iOS and Android.
Key Features of Flutter and Dart
- Cross-Platform Development: Like Xamarin, Flutter allows developers to write code once and deploy it on iOS and Android.
- Fast Development: Flutter’s “hot reload” feature lets developers see changes in real time without recompiling the app, leading to faster iteration cycles.
- Beautiful UI: Flutter provides a rich set of pre-designed widgets that enable developers to create visually appealing apps that follow Apple’s design guidelines.
Drawbacks of Flutter
- Learning Curve: Dart, the language used in Flutter, is relatively new and may require some time for developers to become proficient.
Flutter and Dart Use Cases
If your project demands quick deployment on both iOS and Android, Flutter can be a cost-effective solution. It’s beneficial for startups or businesses that want to test their ideas on multiple platforms without investing in separate native development teams.
5. JavaScript with React Native: A Popular Cross-Platform Choice
React Native is a JavaScript framework developed by Facebook that allows developers to build mobile apps using JavaScript and React. It’s one of the most popular frameworks for cross-platform app development, enabling developers to write code once and deploy it on iOS and Android.
Advantages of React Native
- Cross-Platform Code Sharing: Like Flutter and Xamarin, React Native allows developers to share code between iOS and Android apps, reducing development time.
- Large Ecosystem: As JavaScript is one of the world’s most widely used programming languages, React Native benefits from a large community and abundant libraries and tools.
- Native Modules: React Native allows developers to write modules in native languages (Swift, Objective-C, or Java), which can then be integrated into the React Native codebase for improved performance and access to platform-specific features.
Limitations of React Native
- Performance: While React Native apps are generally performant, they may not match the speed of fully native apps built with Swift or Objective-C, especially for graphics-heavy applications like games.
- Native Knowledge Required: Although much of the development is done in JavaScript, certain functionalities still require knowledge of native iOS development languages.
React Native Use Cases
React Native is ideal for businesses building cross-platform apps while minimizing development costs. IOS app development companies widely use it to deliver robust mobile app development services to clients with both iOS and Android audiences.
Choose the Right iOS Programming Language for Your Project
iOS development landscape offers various programming languages, and the best choice depends on factors like app complexity, performance requirements, and cross-platform compatibility.
When selecting the ideal programming language, consider the nature of your app, the expertise of your development team, and long-term maintenance requirements. Partnering with an experienced iOS development company like EvinceDev can help you navigate these decisions. Their expert team ensures that your app meets user expectations for performance and scalability and delivers a seamless user experience across devices.
With EvinceDev by your side, you’ll have the best tools and technologies to create a high-performing iOS app tailored to your goals.






